Server virtualization is a widely used technology in the IT industry, mainly used in Web Hosting services. Hypervisors are server virtualization software that helps Web Hosting Companies use their resources most effectively.
These hypervisors help run different applications on a single server without needing extra physical resources in dedicated systems. This is a virtual machine that simulates the software and hardware of a computer.
If searching for the best Domain Hosting in NZ, you can opt for different cheap hosting services from NZ Hosting Providers. You can buy NZ Web Hosting at an affordable cost with them.
Let’s learn more.
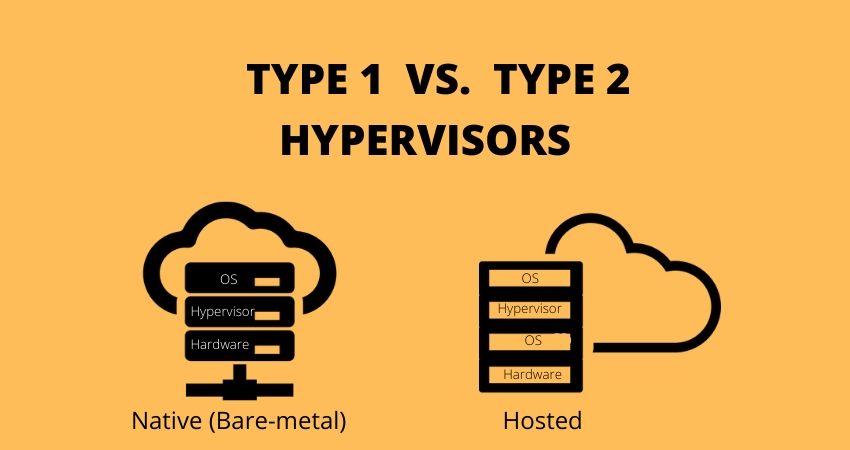
What is a Bare Metal Hypervisor?
Bare metal refers to a server dedicated to a single tenant or user, meaning only you can access its resources. Unlike the cloud model, where multiple users share the same physical server, a bare metal server is exclusive to you. This eliminates the “noisy neighbor” effect, where one user’s activities can negatively impact others on the server.
-
Key Features of Bare Metal Hypervisor
The key features of Bare Metal Hypervisor include:
- Type 1 hypervisor
- Runs directly on server hardware
- Direct access to hardware resources
- High performance and isolation
- Managed through a console or command-line
- Used in enterprise and cloud environments
What is a Hosted Hypervisor?
A hypervisor, on the other hand, is an operating system that enables the creation of virtual machines within a bare metal server. With a traditional bare metal server, the operating system is directly installed on the server, and applications run natively within that operating system.
-
Key Features of Hosted Hypervisor
The key features of Hosted Hypervisor include:
- Type 2 hypervisor
- It runs on top of an OS
- Relies on host OS for resource allocation
- Some performance overhead
- Managed through GUI or command line
- Used in desktop and small-scale scenarios
Differences Between Bare Metal and Hosted Hypervisor
Different types of hypervisors exist, such as bare metal and hosted hypervisors. So, you might wonder which one to choose and how they work. Don’t worry, based on the differences between these two types, you can select the best.
| Parameters | Bare Metal | Hosted Hypervisor |
Underlying Architecture |
Bare Metal Hypervisor, or Type 1, runs directly on server hardware without an OS. | Hosted Hypervisor, Type 2, runs on top of an OS like Windows or Linux. |
Resource Allocation |
Bare Metal Hypervisor provides direct control over hardware resources, offering high performance and isolation. | Hosted Hypervisor relies on the host OS for resource allocation, introducing performance overhead. |
Management and Flexibility |
Bare Metal Hypervisor is managed through a console or command line. | Hosted Hypervisor is managed through GUI or command-line. |
Deployment Scenarios |
Bare Metal Hypervisor is used in the enterprise and cloud environments for critical applications. | Hosted Hypervisor is suitable for small-scale scenarios and running multiple OSs on one machine. |
Conclusion
Both bare metal hypervisors and hosted hypervisors are great options for server virtualization, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific needs. Both approaches are efficient and provide effective resource utilisation of physical servers, enhancing overall hosting performance and improving website performance.
Whether you need to run applications on the server or manage resources for your physical servers, both hypervisors effectively fulfil these requirements.